What Does Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling Do? (Windows 10 & 11 Guide)
Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling lets the graphics card handle its own tasks instead of the CPU. This reduces CPU load, lowers delays, and makes games and apps feel smoother, especially on modern Windows PCs.
In this article, you will learn how hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling works, when it actually improves performance, when it can cause issues, and whether you should enable it on your PC.
What Is Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling?
Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling is a Windows feature that allows the GPU to manage its own workload instead of pushing everything through the CPU. By cutting out some of that back-and-forth, it can reduce delays and make graphics-heavy tasks feel more responsive.
GPU vs CPU Scheduling — The Core Difference:
Normally, the CPU decides which graphics tasks run and when. That works fine until the CPU is already busy. When hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling is enabled, the GPU takes over much of that scheduling work. The result isn’t magic FPS gains, but fewer timing hiccups when the system is under load.
How It Differs from Traditional Scheduling:
Older scheduling methods rely heavily on the CPU for task queues and memory handling. The newer approach hands part of that responsibility to the GPU itself. On modern systems, this can mean smoother frame delivery, especially when gaming while background apps are running.
Key Components Involved:
This feature relies on the GPU’s built-in scheduler, improved VRAM handling, and the Windows Display Driver Model (WDDM). Windows still manages the overall graphics pipeline while prioritizing high-importance workloads more efficiently.
How GPU Scheduling Worked Before This Feature:
Before hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling existed, Windows handled GPU tasks like this:
- CPU receives graphics tasks
- CPU prioritizes and queues them
- GPU waits for instructions
- Tasks are sent one-by-one
This process worked fine, but it created CPU overhead, especially in:
- CPU-limited systems
- High-refresh-rate gaming
- Heavy multitasking
If your CPU is already busy, GPU tasks could be delayed.
How Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling Works Now:
With hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling enabled:
- The GPU manages its own task queue instead of waiting on the CPU
- CPU involvement in graphics scheduling is reduced
- Workloads reach the GPU more directly, with fewer delays
- Delay between tasks can drop, especially under heavy load
Think of it like switching from a middleman system to direct task handling.
In real-world systems, this usually results in smoother frame delivery not necessarily higher FPS, but noticeably better consistency.
CPU vs GPU Scheduling: What’s the Difference?
Here’s a simple way to look at it.
In traditional scheduling, the CPU controls when and how GPU tasks run. With hardware-accelerated scheduling, much of that responsibility shifts to the GPU itself.
| Aspect | Traditional Scheduling | Hardware Accelerated Scheduling |
| Task control | CPU | GPU |
| CPU overhead | Higher | Lower |
| Latency | Slightly higher | Slightly lower |
| Stability | Very stable | Depends on drivers |
| Best for | Older systems | Modern GPUs |
This is why two systems with similar specs can behave very differently once this feature is enabled.
Does Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling Improve FPS?
Sometimes but not in a dramatic way. In most cases, users don’t see a big FPS jump.
What people usually notice instead:
- More consistent frame pacing
- Fewer micro-stutters during gameplay
- Slightly improved input responsiveness
In GPU-bound games, the FPS difference is often negligible. However, in CPU-bound scenarios, the improvement can be more noticeable. This is why results vary so much depending on your hardware, drivers, and overall workload.
Does Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling Improve Gaming?
This feature can help in certain gaming scenarios, but it isn’t a guaranteed boost for every system.
It tends to help when:
- The CPU is acting as a bottleneck
- You are using a high-refresh-rate monitor (144Hz or higher)
- Multiple background apps are running
- You have a modern GPU with well-optimized drivers
On the other hand, you may see little to no benefit if:
- Your GPU is already fully loaded
- You are running older graphics hardware
- Driver support or game optimization is poor
If your game feels smooth but slightly unresponsive, hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling can sometimes improve overall responsiveness rather than raw FPS.
You may also want to compare how different games rely on CPU vs GPU resources in:
Is Fortnite CPU or GPU Heavy? (Complete Guide)
Does Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling Help in Non-Gaming Tasks?
Despite the name, this feature is not just for games, although that’s where most people notice it first.
In tasks like video editing or OBS streaming, it can sometimes make the interface feel more responsive, especially when the system is handling multiple workloads at once.
That said, many professional applications prioritize stability over latency, so improvements may be subtle or vary depending on the software and driver quality.
Pros and Cons of Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling:
Pros:
- Less CPU involvement during graphics-heavy tasks
- Smoother frame pacing in some games, especially CPU-limited ones
Cons:
- Driver quality matters more than most people expect
- On older GPUs, it often makes no noticeable difference
It’s not a “set and forget” feature. Most users decide after testing it in their own setup.
System Requirements and Compatibility:
To use hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling, your system must meet these requirements:
- Windows 10 (version 2004 / May 2020 update or newer) or Windows 11
- A compatible GPU, such as NVIDIA GTX 10-series or newer, AMD RX 5000-series or newer, or recent Intel integrated graphics
- Updated GPU drivers that support hardware scheduling
- WDDM 2.7 or newer, which allows the GPU to manage its own scheduling queue
You can check your current WDDM version using DxDiag under the Display tab.
If your GPU drivers are outdated, update them first before enabling this feature to avoid crashes or system instability.
Related: Intel GPU Drivers: Download, Update & Fix Issues Guide
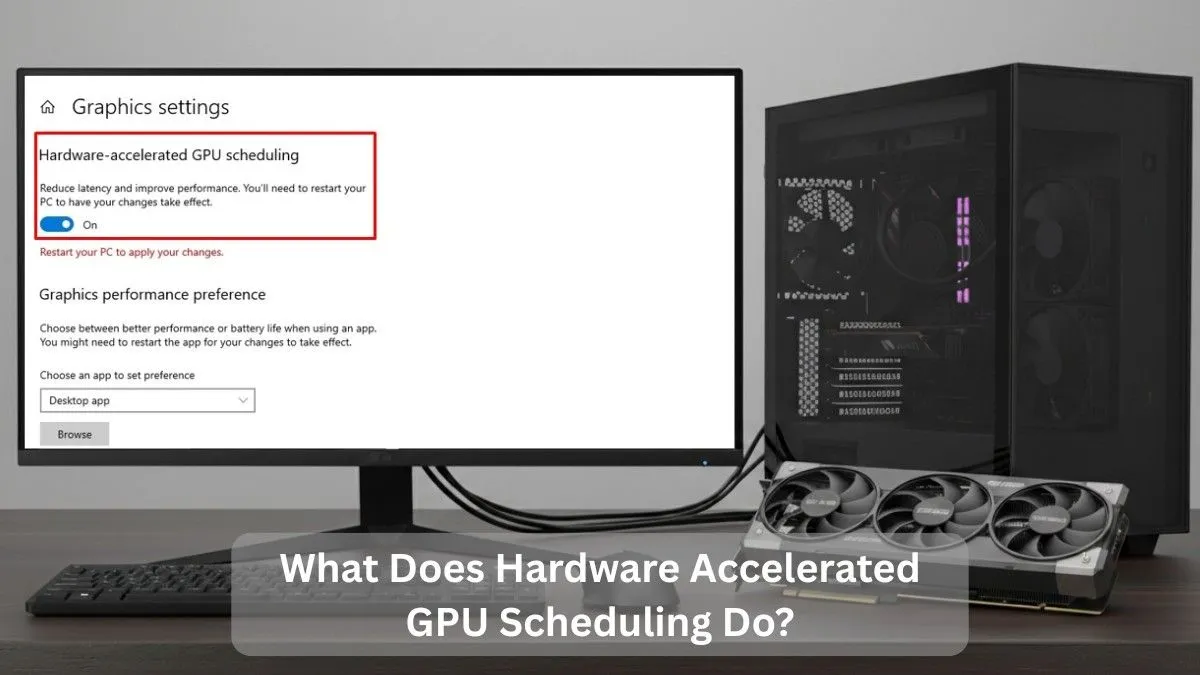
How to Enable or Disable Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling (Windows 10 & 11)

For Windows 10 Step-by-step:
- Press Windows Key + I
- Open Settings
- Go to System → Display
- Scroll down and click Graphics settings
- Toggle Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling
- Restart your PC
For Windows 11 Step-by-step:
- Press Windows Key + I
- Open Settings
- Go to System → Display
- Click Graphics
- Click Change default graphics settings
(On some Windows 11 builds, this may appear as Advanced graphics settings)
- Toggle Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling
- Restart your PC
Common Problems and Troubleshooting Tips:
If you notice any of the following issues:
- Lag or frame drops
- App or game crashes
- No noticeable performance improvement
Try these troubleshooting steps:
- Update your GPU drivers to the latest version
- Disable third-party overlays (such as FPS counters or recording tools)
- Monitor GPU usage and behavior during games or heavy workloads
You can analyze your GPU health and performance using tools like Task Manager, MSI Afterburner, or GPU-Z.
For a deeper check, you can also read How to Check GPU Health – Simple & Expert Guide
Should You Enable Hardware Accelerated GPU Scheduling?
When You Should Enable It:
- You have a modern GPU
- You game or multitask heavily
- Your CPU usage is high during gaming
When You Should Turn It Off:
- You notice instability or crashes
- You are using older graphics hardware
- You see no real performance improvement
There is no universal “best” setting — testing is key.
Best Practices for Maximum Benefit:
- Keep GPU drivers updated
- Monitor CPU and GPU temps
- Avoid unnecessary background apps
- Pair with proper CPU optimization
Small system tweaks can add up to noticeably better performance over time.
Conclusion:
Hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling offloads part of graphics management from the CPU to the GPU, reducing latency and improving smoothness in some workloads. It won’t transform performance, but it’s worth enabling on modern systems. Test it, monitor results, and keep drivers updated for the best experience.
FAQs:
1. What does hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling do in Windows 11?
It allows the GPU to manage its own scheduling queue, reducing CPU involvement and improving frame consistency.
2. Should I enable hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling for gaming?
Yes, if you have a modern GPU and updated drivers.
3. Does hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling increase FPS?
Usually no, but it can improve smoothness and reduce stutters.
4. Can this feature cause crashes?
Rarely, but outdated drivers are the main cause.
5. Is it safe to turn off hardware-accelerated GPU scheduling?
Yes. Disabling it simply returns Windows to traditional scheduling.






